Background
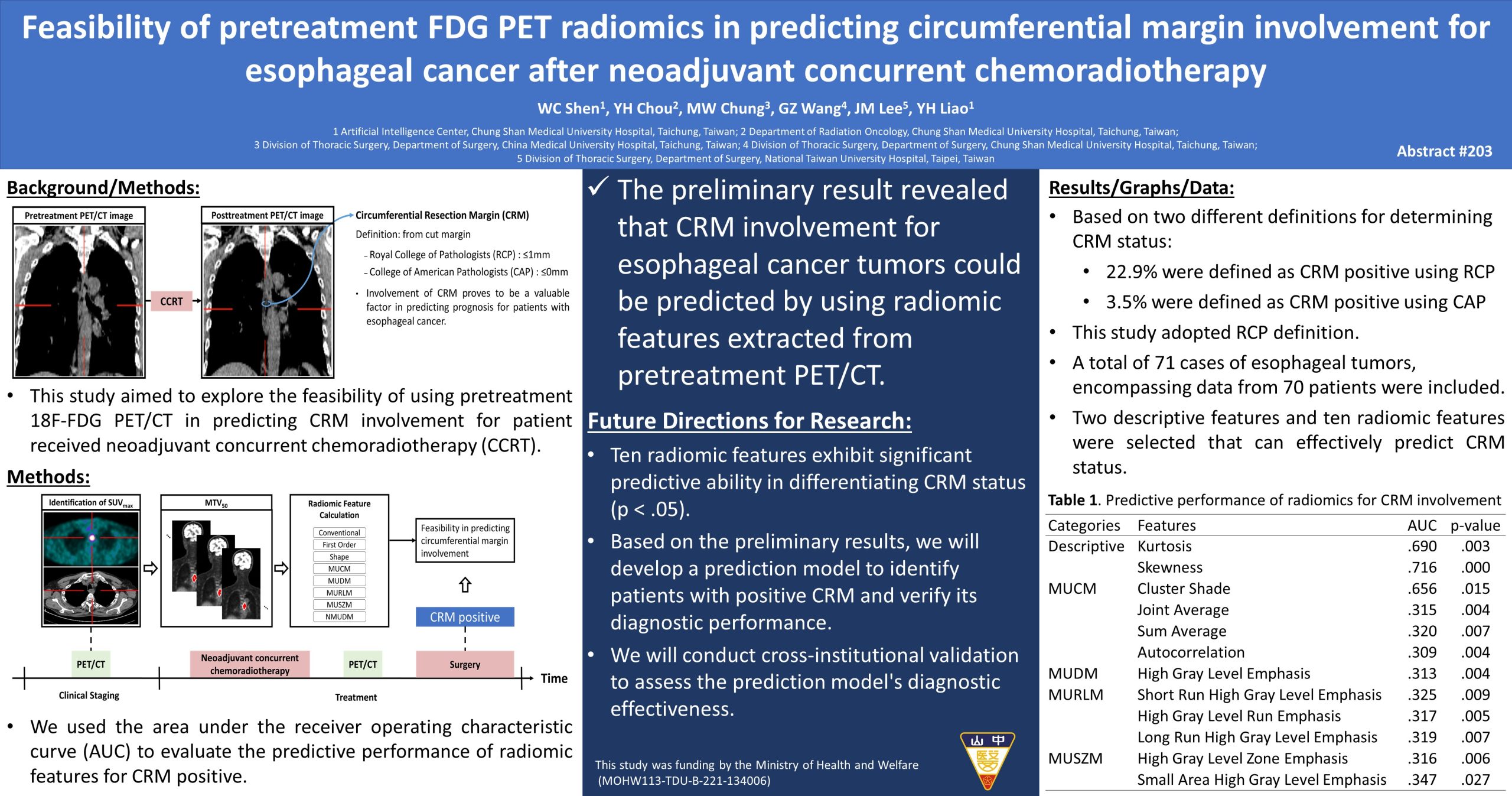
Involvement of circumferential resection margin (CRM) proves to be a valuable factor in predicting prognosis for patients with esophageal cancer. This study aimed to explore the feasibility of using pretreatment 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography (FDG PET/CT) in predicting CRM involvement for patient received neoadjuvant concurrent chemoradiotherapy (CCRT).
Methods
We retrospectively enrolled patients with esophageal cancer who received neoadjuvant CCRT followed by radical surgery between October 2013 and July 2023. All patients received FDG PET/CT examinations before CCRT. The maximum standardized uptake value (SUVmax) within a tumor was identified, and the metabolic tumor volume (MTV) was calculated by using a fixed SUV threshold method (50 % of SUVmax). Descriptive features and five groups of radiomic features (Gray Level Co-occurrence Matrix [GLCM], Gray Level Dependence Matrix [GLDM], Gray Level Run Length Matrix [GLRLM], Gray Level Size Zone Matrix [GLSZM], and Neighboring Gray Tone Difference Matrix [NGTDM]) were further calculated to describe the heterogeneity of the FDG uptakes within MTV. The CRM involvement status was defined by the Royal College of Pathologists (RCP). Tumor presence at or within 1 mm of the cut margin was considered CRM positive. Finally, we used the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) to evaluate the predictive performance of radiomic features for CRM. The significance level was set to 0.05.
Results
A total of 71 cases of esophageal tumors, encompassing data from 70 patients were included. Of the 70 patients, 94% were male with a mean age 58 years across the entire cohort. Sixteen tumors were proved as CRM positive (16/71, 22.5%). Finally, 2 descriptive features and 10 radiomic features were selected that can effectively predict CRM status. These ten radiomic features exhibit robust predictive power for CRM status, demonstrating significance across various discretization bin number. The best performing feature is Skewness (AUC=0.716, p-value<0.0001).
Conclusions
This preliminary result revealed that CRM involvement for esophageal cancer tumors could be predicted by using radiomic features. Future studies are warranted for clinical application.
Publication Year:2024
Conference:2024 ASCO Breakthrough Meeting
Location:Yokohama, Japan